8. Meet the French Royals and their styles: Napoléon Bonaparte
Napoléon proclaimed Emperor of the French in 1804 and reigned until 1814. He achieved many victories, as he was extremely military cunning. He considered himself to be a scientist and when he tried to invade Egypt, he brought along 150 scientists, engineers and scholars to study the history and topography of Egypt.
Mandatory right-hand traffic was introduced in Europe by Napoléon as a strategy to prevent sword fighting on horseback. He could neither dance or sing and he liked to show his affection by pinching people in both ears. Napoléon was so extremely fond of liquorice, that in the last days of his life, he only wanted to drink liquorice flavoured water.
Furniture style: Empire Style
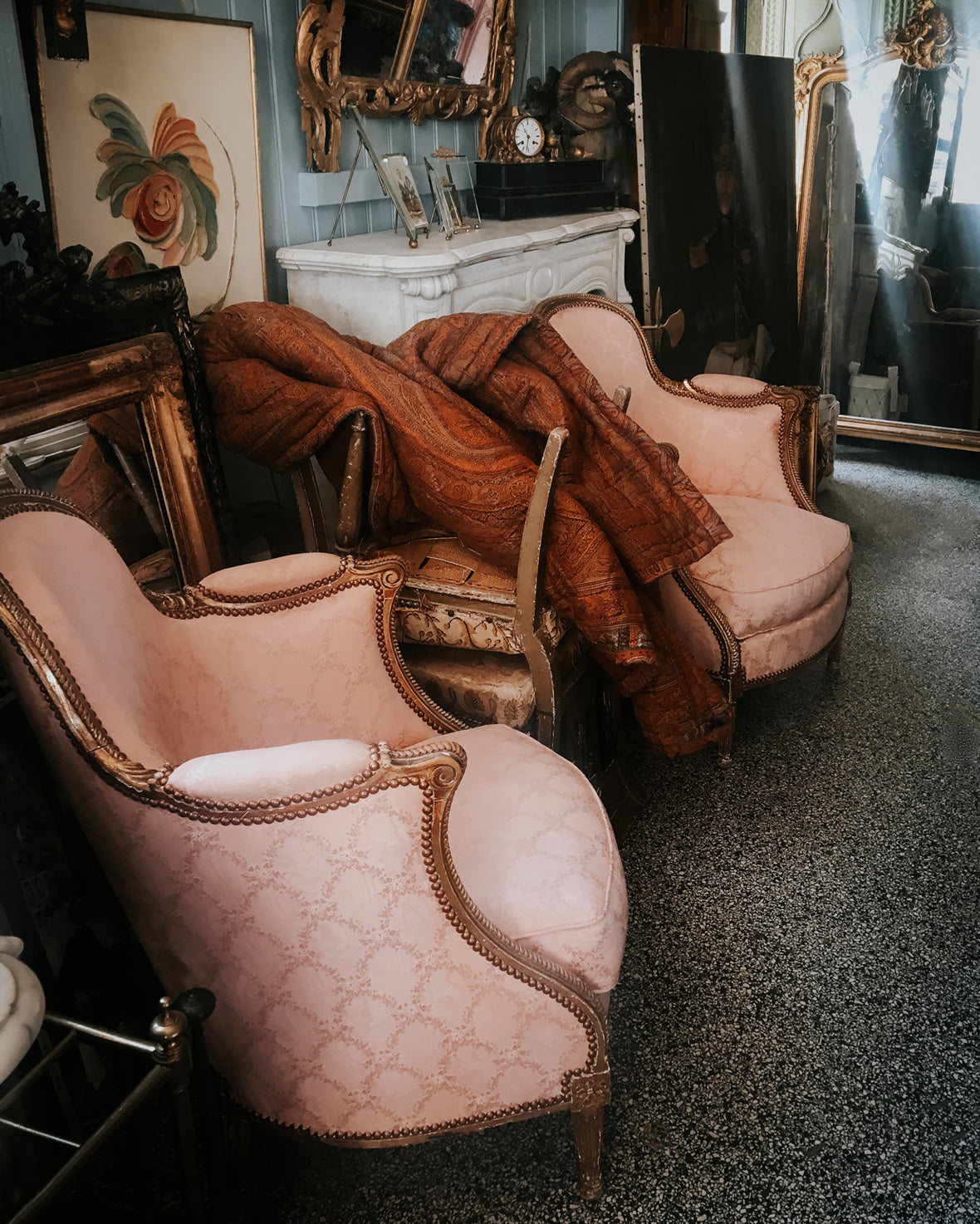
The Empire style, also known as the Napoleonic or Napoleonic Empire style, turned towards the opulence of Imperial Rome, characterized by its grandeur, opulence, and a revival of classical motifs. Very sensitive to luxury and appearances, Napoléon ordered refined furniture for his own residences, but also gave importance to functional furniture adapted to everyday life. Expect straight shapes, highlighted by gilt and chiseled bronze. The inlaid work disappears almost completely. Mahogany is often used, next to walnut, elm and ash. The designs drew inspiration from ancient Greek and Roman symbols: sphinxes, palmettes, bay-tree leaves and laurel wreaths, spears, columns and eagles.
The Empire style favoured bold symmetrical designs. Furniture pieces were often symmetrical in form, with a focus on creating a sense of balance and order.
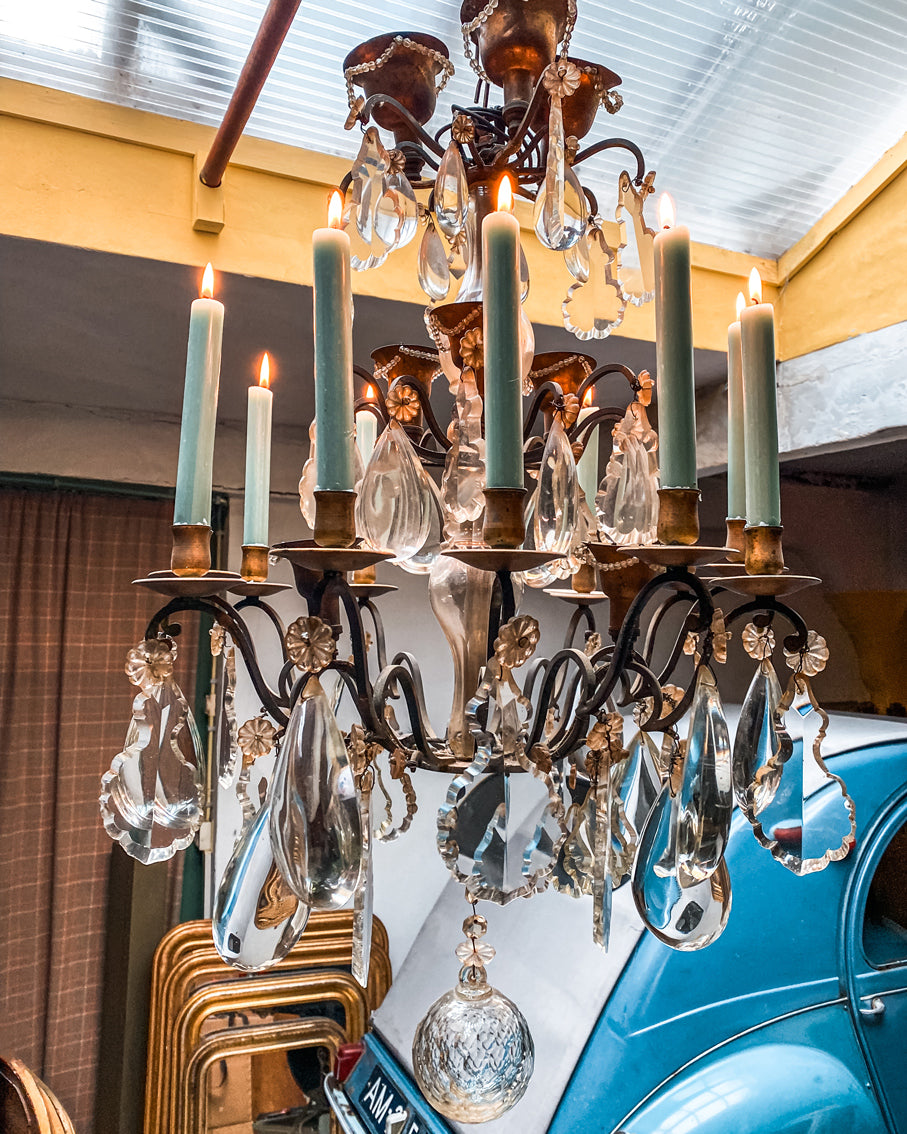
Gold was a dominant element in Empire furniture. Gilding, the application of thin layers of gold, was extensively used to adorn furniture, mirrors, and decorative objects. Ormolu mounts and accents added a touch of luxury.
Empire furniture frequently incorporated animal motifs, such as lions' heads, eagles, and mythological creatures. These motifs symbolized power, strength, and imperial authority.
Dark velvets and damasks were popular choices for upholstery fabrics. Beds in the Empire style were particularly elaborate, featuring tall columns and a canopy. The headboards were often adorned with classical motifs or symbolic elements.
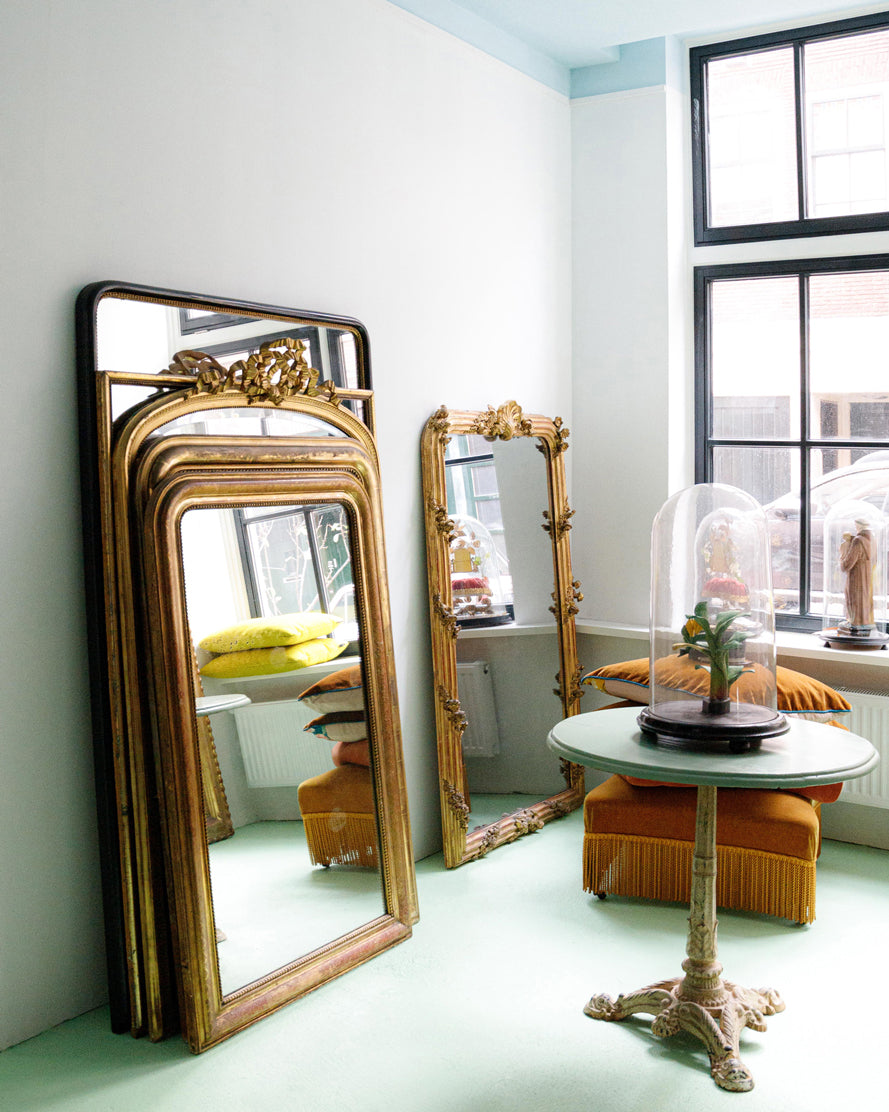
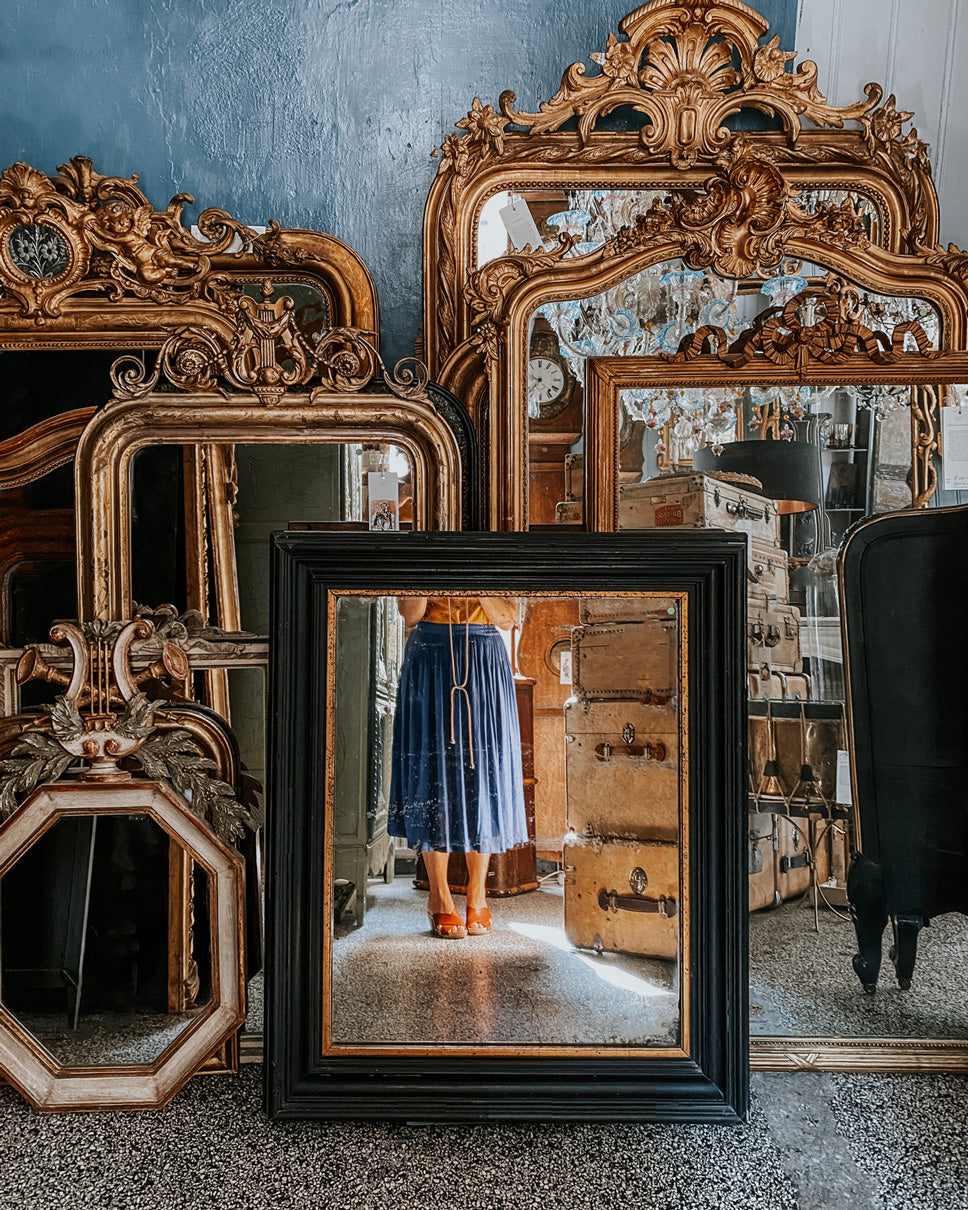
Large Mirrors
Mirrors were a significant element in Empire interiors. They were often large, framed with columns or classical motifs, and served to reflect light and create a sense of grandeur.
Imperial Emblems
Symbols of imperial power, such as the Napoleonic bee and the letter 'N,' were frequently used in furniture and decor to reinforce the association with the Emperor.
The Empire style reflected the political and cultural climate of its time, embodying the grandeur and aspirations of the Napoleonic era. It was a departure from the lightness of previous styles and aimed to convey power, authority, and the classical ideals of antiquity.